How much caffeine is in a single coffee bean? When it comes to coffee, this question often arises.
As a Q-Grader with years of experience cupping coffee from all over the world and conducting sensory analysis, I’ve spent countless hours learning how caffeine content can vary between different types of coffee. The truth is, understanding caffeine in coffee beans is far from simple; it involves looking at the genetics, growing conditions, and brewing methods.
As someone who has dedicated much of my career to studying the intricacies of coffee, I’ve found that the science behind caffeine is not as straightforward as we often think. In this article, we will dive into the science of caffeine in coffee beans, explore how it varies, and uncover what you can control to get the most out of your cup of coffee.
The Basic Answer: Caffeine Ranges in Coffee Beans
The caffeine content in a coffee bean is influenced by various factors, ranging from the type of coffee bean to how it’s processed and brewed. Understanding this is essential for anyone curious about their coffee’s energizing power.
Arabica vs. Robusta: The Fundamental Difference
As someone who has tasted and evaluated thousands of coffee beans, I’ve come to appreciate the differences between Arabica and Robusta coffee beans, two of the most common species found in coffee.
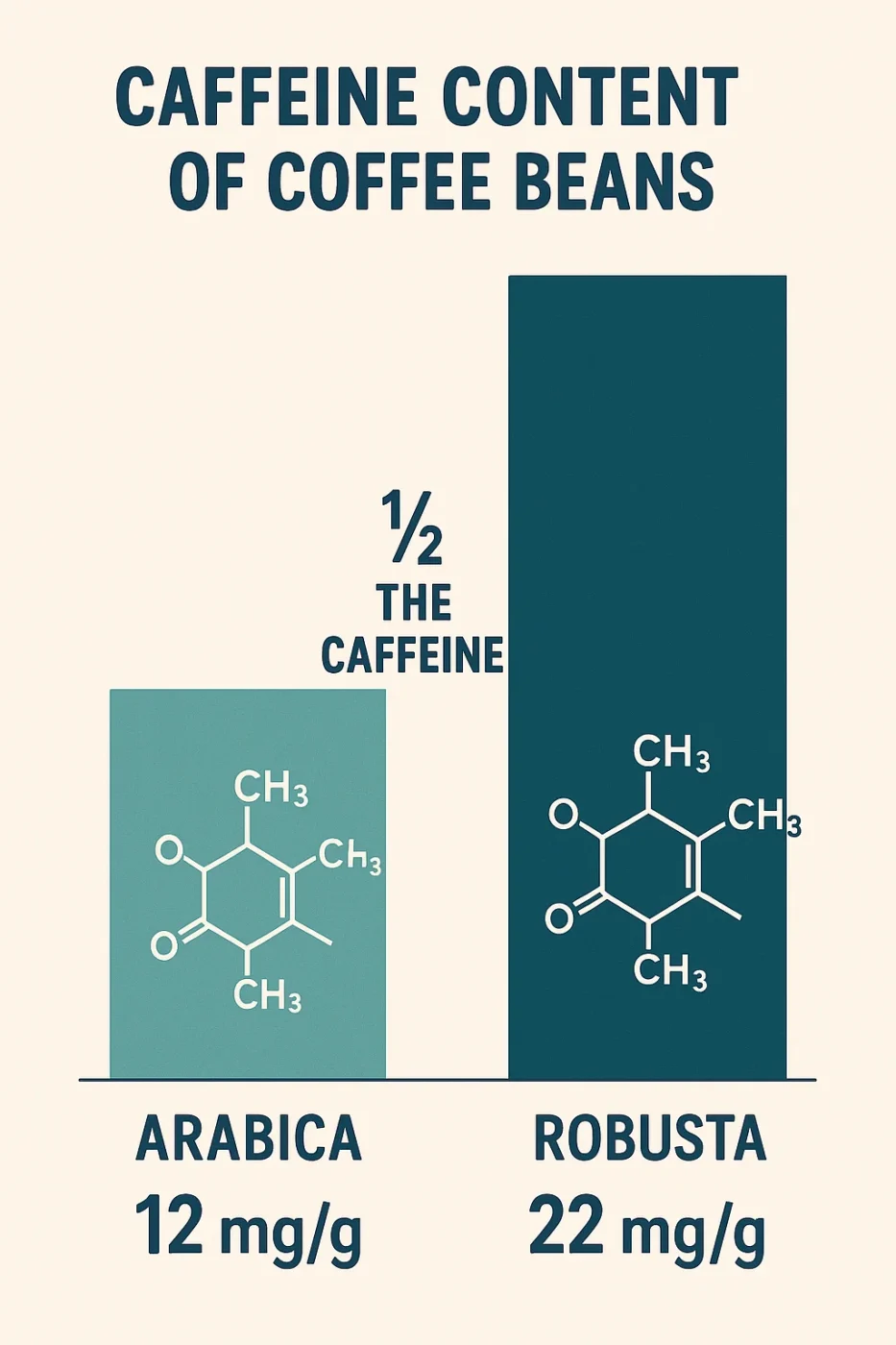
- Arabica Beans: Arabica beans are known for their smooth, complex flavors and are often regarded as superior in taste. However, they generally contain lower caffeine content, about 12 milligrams of caffeine per gram of bean.
- Robusta Beans: Robusta beans, on the other hand, are often used in stronger coffee blends due to their higher caffeine content. They contain about 22 milligrams of caffeine per gram, nearly double the amount found in Arabica beans. This higher caffeine level makes Robusta coffee more bitter and a popular choice for those seeking an extra energy boost.
The genetic makeup of these coffee plants is the primary reason for these differences. Robusta coffee beans produce more caffeine as a natural defense mechanism against pests, while Arabica beans have a more delicate genetic structure that results in a lower caffeine content.
Milligrams per Bean: What the Studies Show
According to the USDA National Nutrient Database, the average caffeine content in a single coffee bean is about 6 milligrams. However, this figure can vary depending on the type of coffee and the bean’s caffeine density. Robusta beans, being denser, pack more caffeine per bean compared to Arabica, which are less dense.
These measurements are consistent with what I’ve observed through sensory analysis and coffee science research. By knowing how much caffeine is in each coffee bean, we can better understand the variability in caffeine content, even within the same type of coffee bean.

Why Caffeine Content Varies: Key Factors Explained
Caffeine content in coffee is influenced by a range of factors, not just the type of bean. In this section, we’ll break down the key elements that affect caffeine levels.
Genetics: The Arabica/Robusta Divide (with DNA-level explanation)
When we talk about caffeine content in coffee, we cannot ignore the role of genetics. Robusta beans are naturally designed to produce more caffeine because it serves as a defense mechanism to ward off pests. This biological trait is a result of evolutionary adaptation.
On the other hand, Arabica beans, though more complex in flavor, have a lower caffeine concentration due to their genetic structure. Studies have shown that Robusta coffee plants have genes that allow them to synthesize higher levels of caffeine compared to Arabica plants.
This scientific insight into the caffeine genetics of coffee plants adds an important layer to our understanding of caffeine content and is a concept often overlooked by other articles. By examining the DNA-level differences, we can better appreciate why Robusta coffee tends to be more bitter and has more caffeine than Arabica
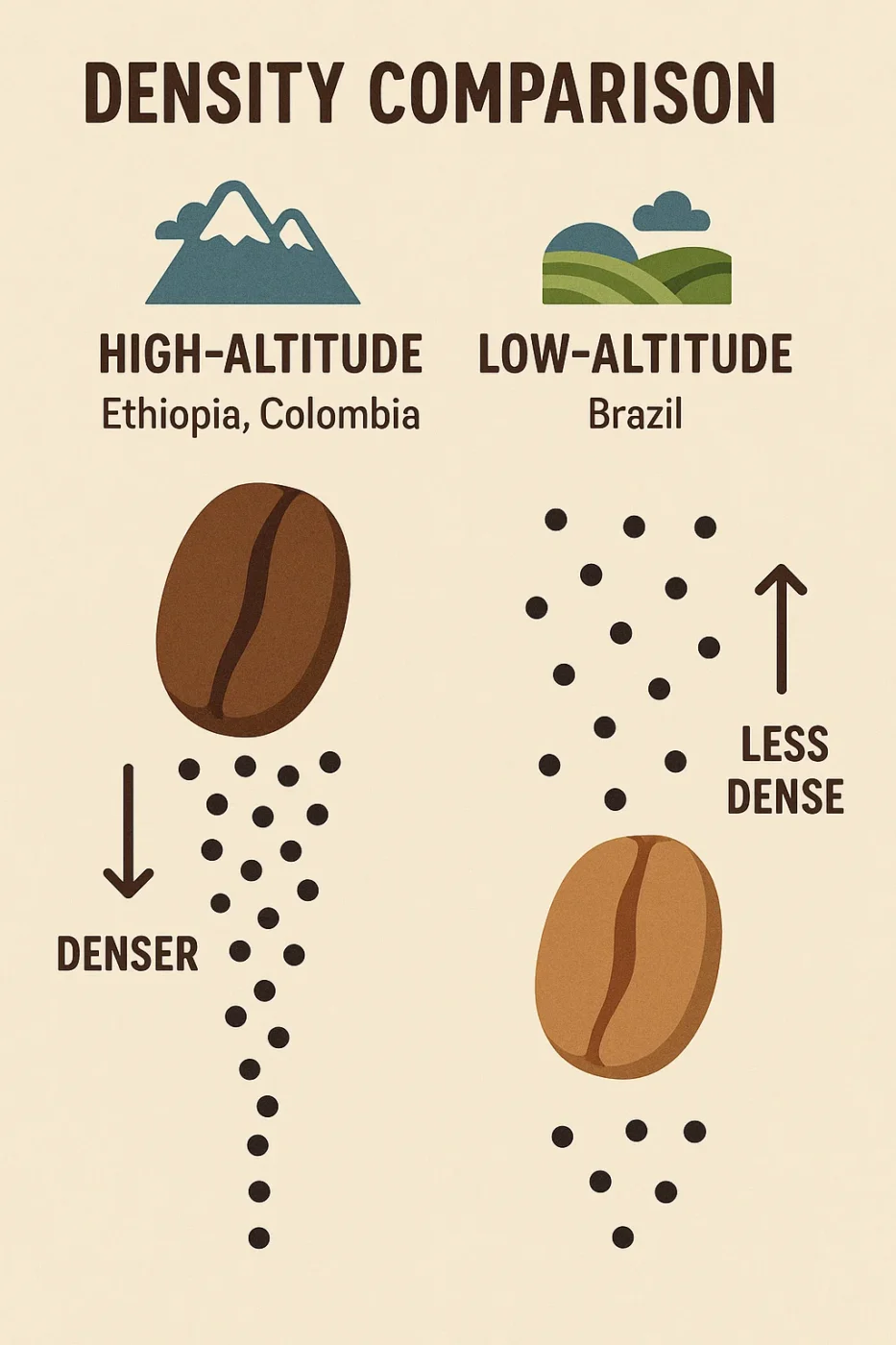
Bean Density and Altitude Effects
Coffee beans grown at higher altitudes are often denser, and this density influences their caffeine concentration. The slow maturation process at high elevations leads to the accumulation of more caffeine in the beans. Beans from regions such as the Ethiopian Highlands or Colombian mountains, which grow at altitudes over 1,500 meters, tend to be denser and have higher caffeine levels.
In contrast, beans grown in lower altitudes, such as those from Brazil, are often less dense and have lower caffeine concentrations. This is a critical factor in how caffeine content can vary, and it’s something many articles miss. Altitude plays a crucial role in caffeine density, which is why understanding a coffee bean’s origin can provide valuable insight into its caffeine content.
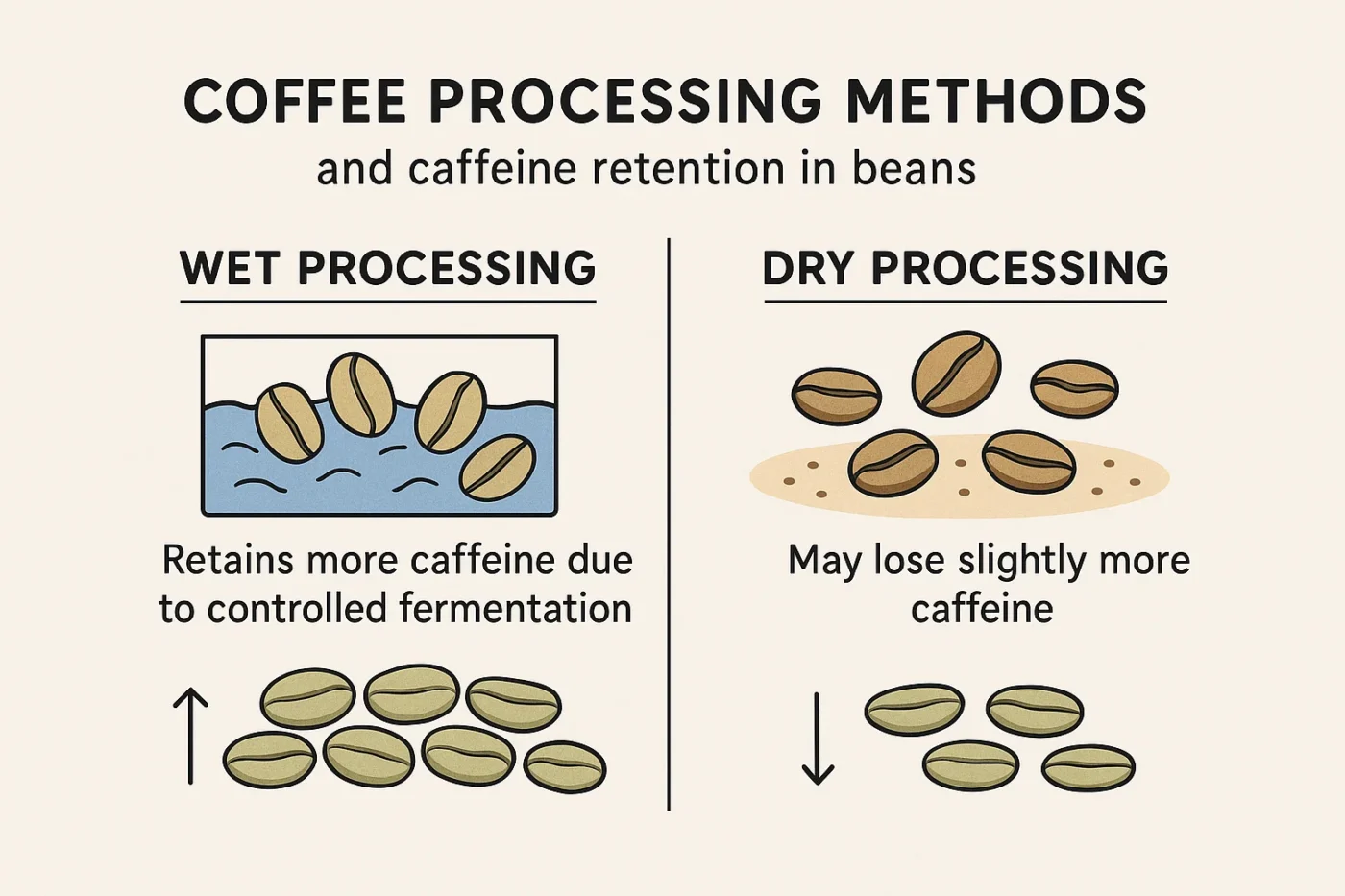
Processing Methods: Wet vs. Dry Fermentation Impacts
The method of processing coffee after it’s harvested also impacts caffeine retention. Wet processing, which is popular in regions like Colombia, helps preserve more caffeine in the beans. This method involves removing the fruit and mucilage before drying, allowing for a cleaner, more efficient caffeine retention process.
On the other hand, dry processing (often used in water-scarce regions) may result in slightly lower caffeine content because the beans are dried with the fruit still attached. This difference in processing methods is an important factor in caffeine variability, something that I’ve seen firsthand during cupping sessions.
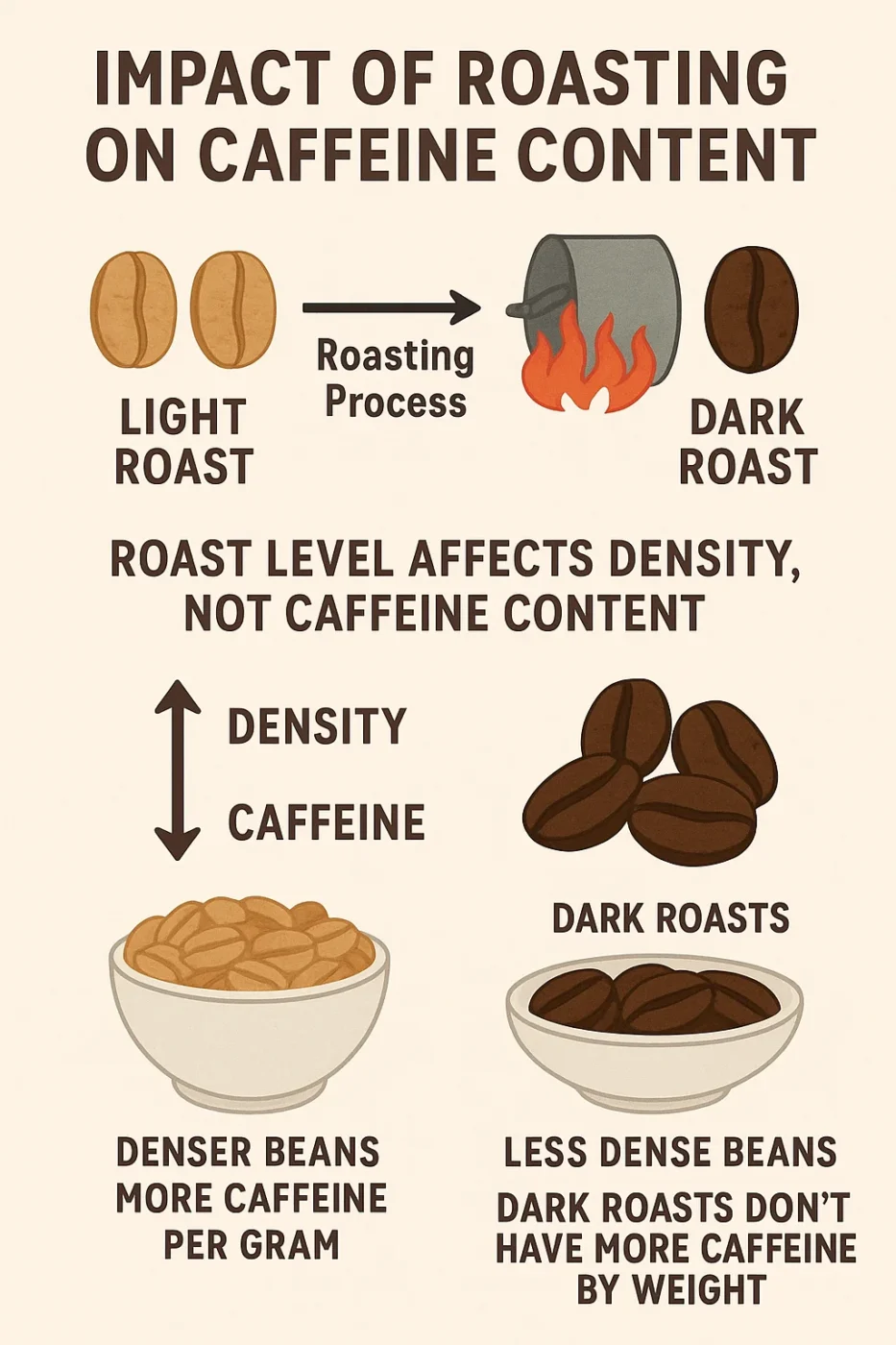
Roast Level Myths vs. Reality (with mass/density science)
One of the most common myths I’ve encountered in the coffee world is that dark roasts contain more caffeine than light roasts. This is not true. The roasting process affects the density of the coffee beans, but it doesn’t significantly impact the caffeine content.
As beans roast, they lose moisture, and darker roasts become less dense. This is why you may need more beans by volume when brewing dark roasts to achieve the same caffeine content as light roasts. However, when measured by weight, both dark and light roasts generally have similar caffeine content. This concept is grounded in the science of mass and density, a crucial factor often overlooked by others in the industry.
From Bean to Cup: Understanding the Caffeine Journey
The amount of caffeine in your final cup of coffee is influenced by more than just the beans. Brewing methods, grind size, and brewing time all play significant roles in how much caffeine is extracted.
How Brewing Methods Affect Final Caffeine Content
Different brewing methods extract caffeine in varying amounts. For instance, espresso, known for its high caffeine concentration, typically contains 63 milligrams of caffeine per shot (1 ounce). On the other hand, methods like French press or drip coffee generally extract caffeine over a longer period, resulting in a higher total caffeine content per serving.
The pressure used in espresso brewing allows for faster caffeine extraction, which leads to a more concentrated shot. However, due to the smaller serving size, you end up consuming less caffeine per shot compared to a larger cup of drip coffee.
Why Bean Caffeine ≠ Cup Caffeine (Extraction Science)
It’s important to understand that the caffeine content in your coffee bean doesn’t always correlate directly to the caffeine in your cup. Caffeine extraction depends on factors like grind size, brew time, and water temperature. For example, fine grounds and longer brew times tend to extract more caffeine. The method you use, therefore, plays a crucial role in how much caffeine ends up in your cup.
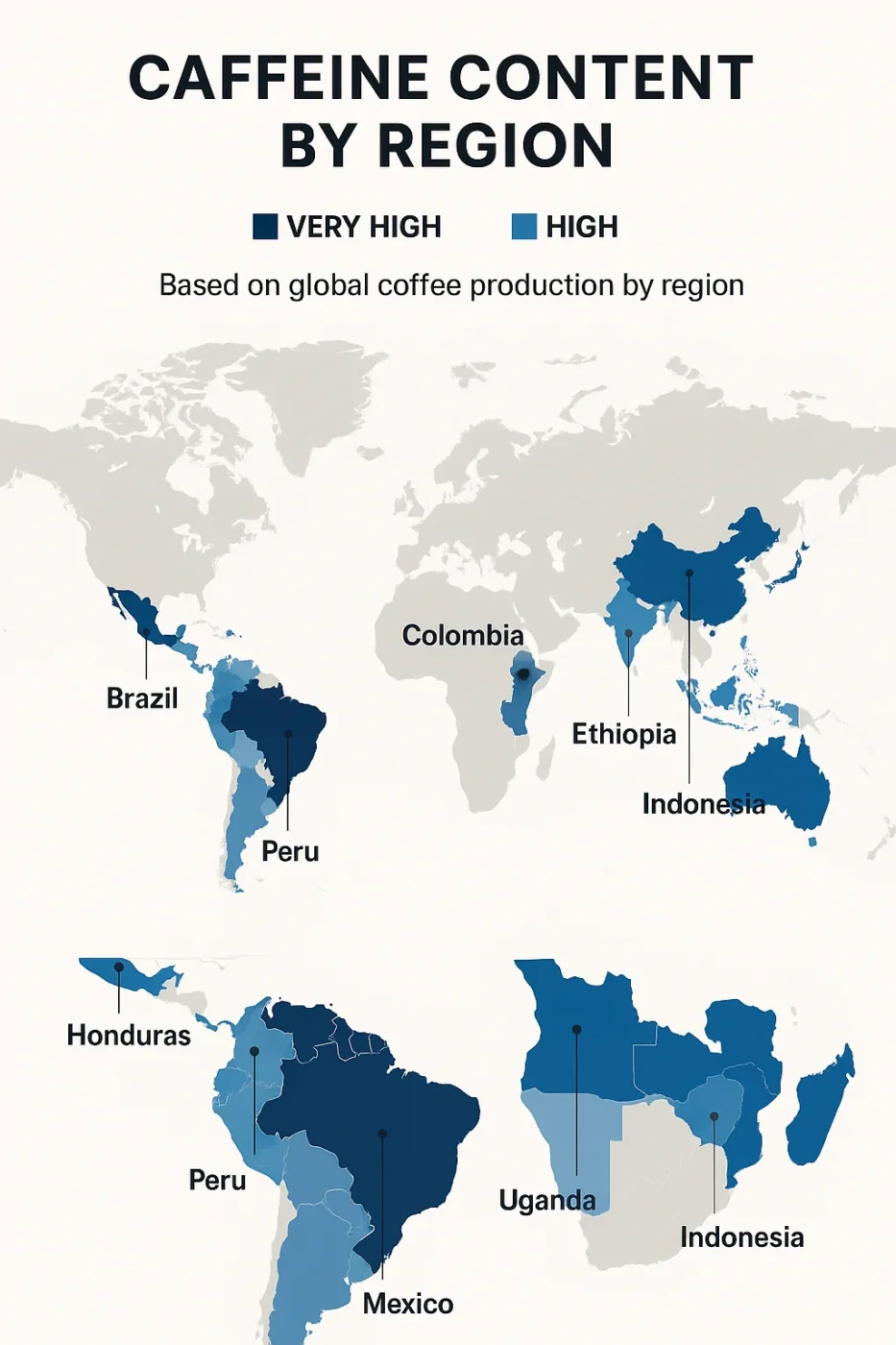
Caffeine Content by Origin: Regional Variations
Caffeine content can also vary based on where the coffee is grown. Altitude, climate, and growing conditions play a massive role in caffeine content. Let’s break it down.
High-Altitude vs. Low-Altitude Growing Regions
As previously mentioned, coffee beans grown at higher altitudes tend to be denser, which can result in higher caffeine content. Beans from regions such as Ethiopia or Colombia, which grow at high altitudes, typically have more caffeine. Beans from low-altitude regions like Brazil often have less caffeine.
Notable Origin Differences (Ethiopian vs. Brazilian vs. Vietnamese)
- Ethiopian Coffee: Known for its high-altitude coffee-growing regions, Ethiopian beans often have higher caffeine content.
- Brazilian Coffee: While Brazil produces a significant amount of coffee, its beans are grown at lower altitudes, resulting in lower caffeine content.
- Vietnamese Coffee: Robusta beans from Vietnam are particularly high in caffeine, offering a stronger brew with more caffeine.
Debunking Common Caffeine Myths
There are several myths surrounding caffeine in coffee that need to be cleared up.
“Dark Roasts Have More Caffeine” – The Truth
As I’ve discussed earlier, dark roasts do not have more caffeine. The density of the beans is the determining factor. Dark roasts lose more moisture and become less dense, so you need more dark beans by volume to achieve the same caffeine content as light roasts.
Decaf Beans: How Much Caffeine Remains?
Even decaf beans contain some caffeine, typically less than 0.3% of the caffeine originally found in the beans.
Espresso vs. Drip: Bean vs. Serving Misconceptions
Espresso may have more caffeine per ounce, but due to serving size differences, a typical cup of drip coffee will generally have more caffeine overall.
What is the role of caffeine in the coffee plant?
Caffeine serves as a natural pesticide in coffee plants. It deters insects from feeding on the coffee cherries, protecting the developing seeds, which will eventually become coffee beans.u003cbru003eCaffeine acts as a defensive chemical, blocking the digestive enzymes of pests and making the cherries toxic. Additionally, caffeine helps inhibit the growth of competing plants around the coffee plant, allowing it to thrive in its natural environment.
How much caffeine is in a typical coffee bean?
On average, a single coffee bean contains about 6 milligrams of caffeine, though this varies depending on the type of coffee. Arabica beans contain around 12 milligrams of caffeine per gram, while Robusta beans pack around 22 milligrams per gram, almost double that of Arabica.u003cbru003eThis difference is primarily attributed to the genetic makeup of the plants, with Robusta beans producing more caffeine as a defense mechanism against pests.
How does altitude affect caffeine levels in coffee beans?
Coffee beans grown at high altitudes generally have higher caffeine concentrations. This is due to the slower maturation process at cooler temperatures, which allows more caffeine to accumulate in the beans.u003cbru003eFor example, coffee from the Ethiopian Highlands or Colombian mountains tends to be denser and has higher caffeine levels compared to beans from low-altitude regions like Brazil. The USDA National Nutrient Database confirms that the caffeine content of coffee can vary significantly depending on where it is grown
What are the differences in caffeine content between Arabica and Robusta beans?
The main difference between Arabica and Robusta beans lies in both caffeine content and taste. Robusta beans have about double the caffeine content of Arabica beans, with 22 milligrams of caffeine per gram compared to 12 milligrams per gram in Arabica.u003cbru003eRobusta beans are typically more bitter and have a stronger, less refined flavor compared to Arabica, which is smoother and more complex in taste. This higher caffeine content in Robusta beans is a natural defense mechanism for the plant against pests.
Does the roasting process affect caffeine content in coffee?
The roasting process does not significantly change the caffeine content in coffee beans. What roasting does affect is the density of the beans. Darker roasts tend to be less dense because they lose more moisture during the roasting process. Light roasts, on the other hand, are thicker, meaning that by weight, they contain slightly more caffeine than dark roasts.u003cbru003eHowever, if you measure by volume, dark roasts may appear to have more caffeine because they require more beans to reach the same weight.
What is the difference between caffeine in espresso and drip coffee?
Espresso has a higher concentration of caffeine per ounce compared to drip coffee, with about 63 milligrams of caffeine per shot (1 ounce). However, because espresso is typically served in smaller amounts, the total caffeine content in a serving of drip coffee is often higher.u003cbru003eFor instance, a typical 8-ounce cup of drip coffee contains around 95-200 milligrams of caffeine, depending on the brewing method. So while espresso is more concentrated, drip coffee generally provides more total caffeine per serving.
Does decaf coffee still contain caffeine?
Yes, decaffeinated coffee still contains a small amount of caffeine, usually less than 0.3% of the caffeine content found in regular coffee.u003cbru003eThe decaffeination process removes most of the caffeine, but some residual amounts remain in the beans. For those looking to reduce their caffeine intake without cutting out coffee completely, decaf is a good option, but it’s not entirely caffeine-free.
How do processing methods affect caffeine content?
The method used to process coffee after harvesting can influence the amount of caffeine retained in the beans. Wet processing, common in countries like Colombia, tends to preserve more caffeine because the beans are washed and the mucilage is removed before drying.u003cbru003eIn contrast, dry processing (used in regions with less water) can result in slightly lower caffeine content as the beans are dried while the fruit is still intact.
Conclusion
Understanding the caffeine content in coffee beans isn’t as simple as picking a bean and brewing it. From the genetics of the coffee plant to altitude effects and brewing methods, caffeine content can vary significantly. By considering these factors, you can make better decisions about your coffee choice to suit your caffeine needs. Whether you prefer a mild cup or a high-caffeine brew, understanding the science behind it will help you optimize your coffee experience.
If you want to enhance your brewing skills, check out our guide on the best way to prepare coffee at home, which offers tips and tricks to elevate your daily cup. Want to explore more about the different drinks you can make? Visit our article on different types of coffee drinks to discover new favorites. For those who prefer a caffeine-free experience, you can also check out our list of Starbucks drinks without caffeine (hot & cold). Finally, if you’re using the Baratza Encore grinder, explore our detailed grind settings guide to optimize your grind for the perfect brew.
Want to explore more about caffeine and how it affects your brew? Try our interactive caffeine calculator (will be launching soon) to discover how brewing methods and bean types influence caffeine extraction.


Pingback: A Complete Guide To 4 Different Types Of Coffee Beans
Pingback: Does Ryze Mushroom Coffee Have Caffeine? 2025 Best Guide